Benefits of GIS in Urban Planning
调查土耳其埃斯基塞希尔的擅自占地定居点
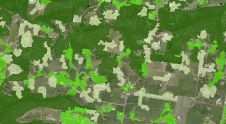
传统的信息管理方法在有问题的城市地区(例如棚户区定居点)的计划过程中很难使用。GIS提供了动态查询和分析,信息显示和更易于理解的表示的能力。经过introducing GIS,the authors analyse the social and infrastructure possibilities of the squatter settlements in Eskisehir Municipality. They determine areas with inadequate public services and infrastructure, and provide basic solutions.
The problems of large metropolitan cities have been comprehensively studied by many researchers. Nevertheless, a country that just consists of a few very large urbanised areas arbitrarily embedded in a rural context is not viable and not optimally sustainable. A network of medium-sized cities that are evenly distributed over the territory is more feasible. Therefore it is important to also investigate the problems of these smaller cities. The city of Eskisehir, Turkey, has been chosen as a case study. This city is located in the northwest of Anatolia at an equal distance from the primary metropolis Istanbul and the capital Ankara.

土耳其的城市Eskisehir
Demography: increase people living in urban areas
土耳其的城市人口已从1985年的2360万增加到2000年的4410万。在这15年期间,居住在城市地区的人群比例从45.2%增加到65.1%。这些数字表明,尽管土耳其的城市化水平低于西方国家的增长率很高。令人担忧的结果之一是低收入家庭在擅自占地的地区不受控制的定居点。住房是一项基本的人类权利,但如果没有有效的控制,则可能会损害生态平衡。直到1970年代,在埃斯基塞希尔(Eskisehir)的建造不常见。由于迅速的工业化,住房库存在1970年代之后变得不足,棚户区的定居点开始集中在工业场所和主要道路周围。如今,约有30%的人口居住在棚户区。1997年,超过154,000人居住在16个棚户区,而在2000年,这一数字增加到了近169,000人。经常非法将土地分为包裹的物业开发商使定居点变得容易。开发人员并没有为建造基本服务而付出太多努力,因为他们的主要利益是利润。 they are not concerned with living standards or environmental balance.
Planning and GIS
计划包括确定适当的未来ecisions and actions through a series of choices. Making choices requires, in addition to thorough planning knowledge, comprehensive (geo-)data about the past, present and future. The information may be descriptive, predictive or prescriptive in nature. Appropriate and efficient management of information greatly improves the quality of planning. Generation of the proper type of information is very difficult with manual methods. GIS provides many basic functions for appropriate and efficient management of geo-information. Essentially, GIS supports the collection, maintenance, analysis and display of spatially related information. GIS data enable multiple viewpoints to be considered and provide the capability for dynamic query and display of information, and a more understandable representation. On the other hand, the accessibility of digital data may cause abuse and misuse, raising fundamental issues of data security, responsibility and reliability.
了解计划区域
Statistics, reports, articles, aerial and close-range photos, satellite images, maps and drawings all aid in understanding the planning area and its problems. Alternative solutions may be developed by importing this data into computer models. These models may predict, for example, demographic changes and land use modifications or simulate traffic flow. Often these computer models are implemented as stand-alone software. GIS facilitates by providing digital geo-data and display of intermediate and final results. Arriving at the most appropriate solution requires communication and collaboration among many stakeholders. Communication is best done through visualisations such as images and maps rather than through bare text. GIS is a perfect visualisation aid. So, GIS makes model creation and interpretation easier and provides understanding that may otherwise not be achieved.
Database
A database was created by an extensive survey of land use and population statistics of Eskisehir. All analogue maps and plans were scanned, and blocks and buildings digitised. Numerical data were converted into tables, graphs and maps. A basic image and GIS layers were created as thematic maps in a topological data structure. Topologically coded geo-data enables spatial query and analysis whilst large and complex sets of diverse data types can be efficiently managed. Issues such as insufficiency of public services and infrastructure and accessibility of public services can in this way be addressed more easily than by traditional methods. All the themes such as districts, public facilities, blocks and houses were stored as separate layers, which can be easily represented graphically. Many layers were created using the basic image as source. Data created with the Turkish GIS software package NetCAD were converted to data compatible with ArcGIS 8.3.
Analysis
The analysis and overview are based on relevant literature, amnesty laws, statistics from the State Statistics Institute created in 2000, maps, master plans and reconstruction improvement plans (upgrading), field surveys, data from concerned authorities and from the reports written by these authorities and organisations. The parameters used during analysis included:
- population
- number of storeys
- 根据规划标准的公共服务足够
- walking distances to public services
- 公共服务领域。
From the descriptive information such as infrastructure, population data and area of the districts, the following parameters were derived:
- floor area coefficient of the houses
- 在不受控制的定居点中存在基本服务和基础架构。
结果
As a result of legislation of squatters by amnesty laws and weakened fear of demolition of houses, the number of the squatters has increased year after year. After the last amnesty laws, municipalities were allowed to upgrade district plans and increase the number of storeys to four. Compared to standards and law, public services are inadequate; the ratio of services to the number of people is low and walking distances are too high. Even the ratio of proposed public services to the existing population is too low according to the standards defined in developmental regulations. While 98% of the houses in 1989 had a septic tank, in 2002 60% of the houses were connected to the sewer system, 39% had a septic tank and 1% did not have any disposal system. Nearly all buildings have electricity and indoor running water (99.2% and 91.5%, respectively). These proportions are larger than Turkey’s average. None of the districts are connected to a source of natural gas. Suitability factors, factor scores, factor weights and permitted land use conversions can be specified for all land use by using GIS. Automated mapping allows the efficient handling and dissemination of thematic information enabling quick map making for planning and decision making.
结论
在可预见的将来,埃斯基塞希尔的住房需求将增加。为了防止将来的擅自占地者定居,必须进行以下操作:
- Eskiºehir Municipality should take preventive measures by identifying possible development areas for settlement in agreement with development of industrial sites, housing areas proposed in the master plan, municipal services, public land and the transportation network
- after identification of settlement areas, site and service specifications should be ensured by constructing roads, water and electricity supply, drains and sewerage, layout of plots and service areas
- the use of GIS techniques should be stimulated to support settlement development by using planning models and scenarios and proper data in digital format.
Google Maps: Eskisehir
Make your inbox more interesting.Add some geo.
Keep abreast of news, developments and technological advancement in the geomatics industry.
Sign up for free