放大细节
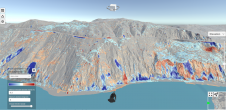
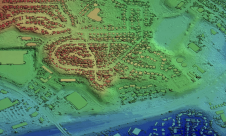
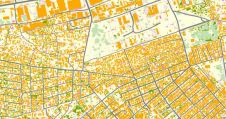
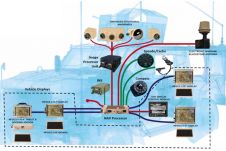
如今的政治趋势集中在智慧城市、可持续性交通、生活质量以及增强本应是世界上独一无二的地方特色上。例如,卡塔尔就有举办全球体育赛事的重大计划。上海正成为世界上最大的港口,而香港已超过孟菲斯机场,成为世界上货运量最大的机场。大城市和其他人口稠密地区的管理需要在很大程度上依赖权威地理数据的决策。由于这些决议将塑造未来几年的城市景观,所以数据必须是准确、详细和最新的。与此同时,为了跟上政治野心的步伐,对收集、存储和传播地理信息的新技术的探索正以惊人的速度进行着。由此产生的趋势是:(1)关于建筑、基础设施和农业用地及其2D和3D属性边界的详细数据的收集越来越多;(2)集中于某一特定用途的小规模调查迅速增加;(3)混合不同的地理数据集,(4)提供基于地理数据的集中服务。这类服务深受规划者、建设者、企业和公众的欢迎。 For example, inputting accurate spatial data into a Building Information System (BIM) requires detailed surveying of sites and objects. In turn, the need to raise output and cut costs is triggering the advance of innovative methods such as indoor positioning, unmanned aerial surveys and oblique aerial photogrammetry. At times these technologies are used on their own, but they may also be added to proven techniques such as terrestrial laser scanning. Indeed, governments want to gather more and more facts about buildings and other constructions within their jurisdiction. The UK, for example, has defined six attributes (sub-structure, roof type, walls, age, land use and number of floors) for classifying commercial premises, community facilities and other kinds of non-residential buildings. The majority of this information can be derived from visual inspection of oblique aerial imagery.
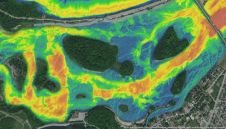
亲密的Penchant不仅限于砖和砂浆。例如,森林群体也热衷于降至一棵树的水平,以监测增长,健康和记录。全波形空气传播激光器与多光谱卫星图像相结合,可以满足这种需求。由于质量可能是由于粗糙分辨率而令人瘢痕,因此将LIDAR和由(倾斜)相机捕获的多光谱图像结合的空中调查可能会带来浮雕。超越地理数据的服务也在需求,如英国地质调查最近推出从核心地质数据集的地图推出,以供给规划者和环境研究人员。实际上,我们收集,管理和使用地理数据的方式正在迅速变化。因此,Geomatics无疑将忍受作为研究人员,从业者和学生的剧烈专家领域,因为越来越多的呼吁在细节上缩小。