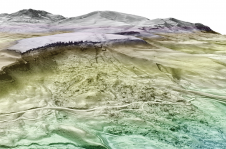
填补Goce数据差距发掘南极的地质过去
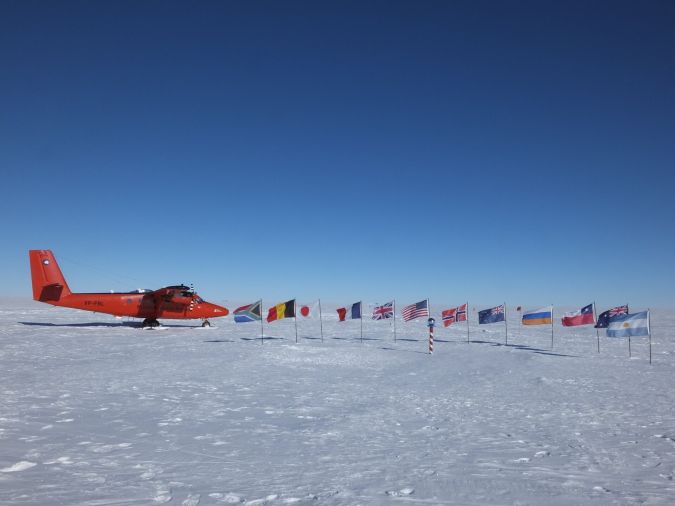
ESA资助的名为Polargap的运动使用空中传感器进行了多种测量,以填补北极和南极卫星覆盖的空白。
It is very difficult to know what lies beneath a blanket of kilometres-thick ice, so it is hardly surprising that scientists have long contested the shape and geology of the ancient supercontinent from which East Antarctica formed over a billion years ago. An ESA-funded study can now lay some of this conjecture to rest.
科学家在冰下使用传感器来测量冰下不同岩石的重力和磁性特征的变化,科学家发现了一个巨大的海湾,英国的大小形成了南极洲东部边缘的一部分。
Satellites orbiting Earth from pole to pole don’t actually fly directly above the North and South Poles. This leaves two small circular gaps in the global data. To fill in these missing measurements for ESA’s GOCE gravity satellite mission over the South Pole, an international team of scientists joined forces to take a multitude of measurements from aircraft as part of an ESA campaign called PolarGAP.
相等重力的表面
GOCE任务以无与伦比的精度绘制了地球的重力,并提供了有史以来最准确的“ Geoid”模型,以进一步了解我们对地球工作原理的理解。地质是由重力场定义的相等重力电位的表面 - 对于得出准确测量海洋循环和海平面变化至关重要,这两者都受到气候变化的影响。因此,重要的是要填充Goce由于其轨道而无法在极点上进行的测量。
一种s well as supplying this missing data for GOCE, the PolarGAP team has yielded new insights into the hidden geology at South Pole, shedding new light on the extent and shape of the edge of East Antarctica.
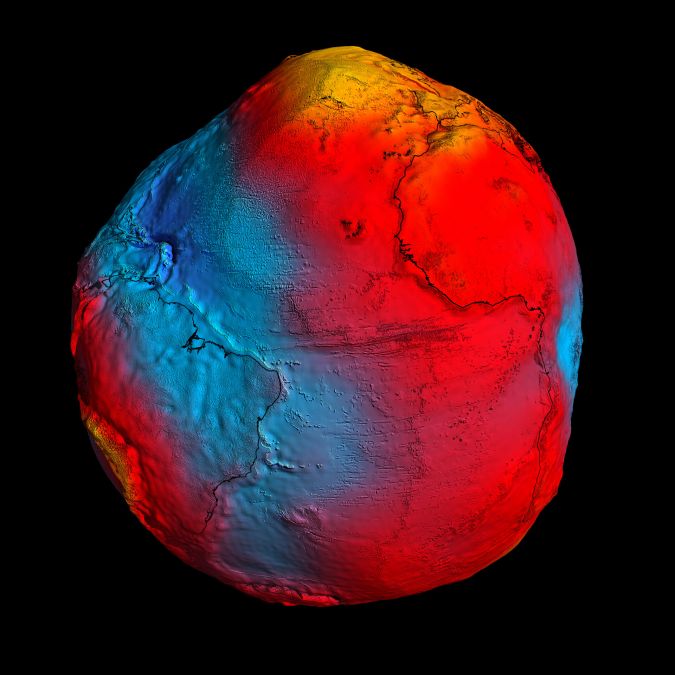
How the Edge of East Antarctica Evolved
一种paper, published in大自然通讯地球和环境,描述了如何团队飞过南极东部and used airborne sensors to measure changes in the magnetic and gravity signatures produced by the different rocks hidden beneath the ice.
The data they gathered along these flight paths enabled the team to determine key characteristics of the rocks, which provided tantalizing new clues about how the edge of East Antarctica evolved. This is important because East Antarctica is the least known region of Earth. Today, Antarctica is isolated from the rest of the world. But a billion years ago, before the ancient Pacific Ocean formed, East Antarctica may have been much closer to other huge landmasses, including North America – an idea that is hotly debated by geologists.
令人惊讶的是,新数据表明,古代岩石的大小像英国的大小一样,被认为也构成了南极洲东部海岸的一部分,完全缺少。取而代之的是,他们发现了一个由年轻岩石组成的嵌入,该岩石比预期的。这种新发现的胚胎称为pensacola胚胎。
This means that less of East Antarctica than was previously assumed formed part of the ancient Mawson Continent, which included part of East Antarctica and Australia, and which is inferred in some reconstructions to have been close to North America.
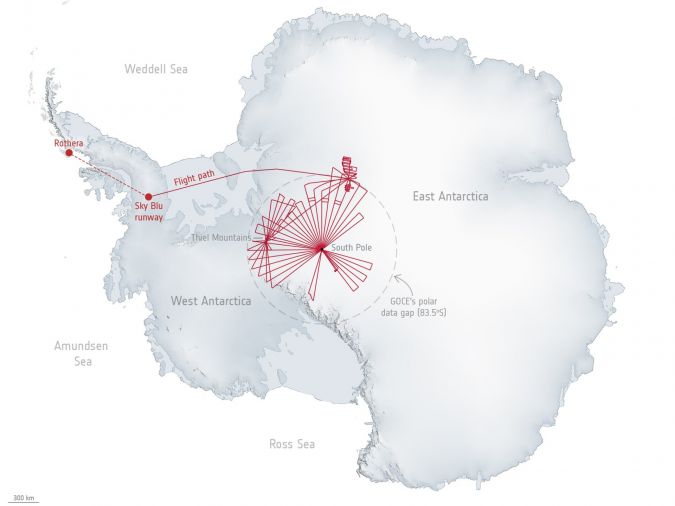
The consequences of this finding will form the basis for a wide range of Antarctic research. It will help researchers build global reconstructions of Earth’s ancient supercontinents and lead to a better understanding of how the ancient geology of East Antarctica influences the flow and stability of the modern ice sheet.
下图显示了新发现的高度磁性岩石(红色的阴影)以及这些岩石似乎缺失的区域。
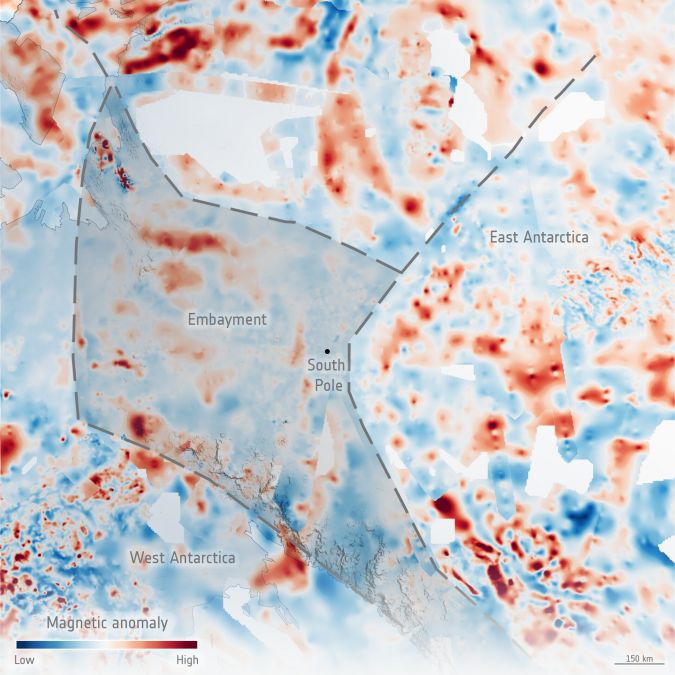
地热热通量
英国南极调查的首席作家兼地球物理学家汤姆·乔丹(Tom Jordan)博士说:“好像已经从南极洲东部被带走了。这可能发生在一次重大裂谷活动中,可能与大约6.5亿年前的古代太平洋开放有关。
“The embayment in the South Pole region subsequently influenced how mountain ranges and volcanoes developed in the area, and the scars at the edge of where the embayment formed continue to guide the flow of the present-day ice sheet.”
美国国家海洋研究所和应用地球物理学院和极性研究人员的Fausto Ferraccioli博士补充说:“找出南极craton东部的边缘所处的边缘有助于限制古代超邦内斯塔东部东极地区的范围。
“And, what interests me most for current ESA research – edges of cratons also exert a key influence on geothermal heat flux. Lower values are typically found on the craton side compared to younger embayments. The new data will help determine if this is also the case at the South Pole, with cascading implications for understanding how this affects the water that flows beneath the East Antarctic Ice Sheet.”
国际协作ESA PolarGAP运动使这项研究成为可能。该运动的主要目的是扩大南极周围极地间隙地区的Goce卫星重力场,那里缺少卫星测量。但是,由于对PolarGap进行了仔细的调查设计和规划,因此在南极洲东部的这一以前未开发的边境中出现了广泛的科学结果。
Source: ESA.