Bringing Colour to Point Clouds
Developments in Multispectral Lidar Are Changing the Way We See Point Clouds
到目前为止,大多数可商购的机载LiDAR系统已经在一个单个波长上运行,反映了脉冲的能量,然后将其用于分类或可视化。新的开发产生了第一个多光谱激光痛系统,该系统使用激光脉冲扫描许多不同的波长。多光谱LIDAR数据包含有关扫描对象的有价值信息。该领域的快速发展进步可能代表激光雷达系统的下一个技术飞跃。
(由Sam Fleming,Iain H. Woodhouse和Antoine Cottin)
激光雷达系统从根本上改变了映射和测量的世界。机载系统可以覆盖大面积和偏远的地方,而地面系统可用于室外和内部建筑物内部详细扫描。ICESAT卫星甚至表明LiDAR技术可用于从空间中映射。自从引入第一个LiDAR系统以来,已经有许多技术发展,例如空气中的多个脉冲和全波形记录,下一个主要的发展很可能是多光谱激光雷达。
Images and Lidar
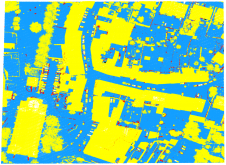
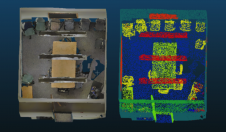
多光谱成像数据已经使用了数十年。除了可见的红色,绿色和蓝色值之外,这些数据集还包含电磁频谱红外许多其他波长的反射数据。该技术依赖于对大量不同波长敏感的相机。可以在四个波长之间拾取的摄像机称为“多光谱”,而“高光谱”一词应用于能够记录20多个波长的摄像机。多光谱成像数据用于通过光谱响应(例如识别不同植物物种)对区域或对象进行分类。近年来,将这种多光谱数据与LiDAR数据相结合的兴趣越来越大。这可以通过将LIDAR数据与单元大小类似于多光谱数据的栅格进行电磁线来完成。或者,可以应用一种查找方法来从每个激光点的多光谱数据中找到相应的值。图1显示了通过将点与空中图像融合的点云的示例。
Passive or active
Current multispectral imaging systems work on the principle of passive remote sensing. They detect the sunlight that is reflected from a surface towards the camera. Hence, the data recorded is highly dependent upon the light conditions, the position of the sun and the way the sunlight is reflected in all directions by the surface material. Conversely, Lidar is an active remote sensing system which detects the reflected laser light emitted by the sensor itself. It is independent of light conditions and can even work in the dark. An active system capable of sensing multispectral data is of great interest to scientists and professionals since it can provide multispectral data that is independent of solar illumination or the reflectivity of a surface material. Active systems can also benefit from multiple returns from a single pulse, thus making it possible to see beneath higher-lying points.
多光谱激光雷达
Conventional Lidar systems operate on a single wavelength, usually in the infrared part of the spectrum. To obtain multispectral Lidar, one option is to fly multiple Lidar systems using different wavelengths simultaneously. This necessitates access to the multiple Lidar systems, and also to an aircraft which can carry multiple systems and provide the associated power supply. This set-up results essentially in a number of overlapping point clouds. A point in one of the point clouds will not be exactly coincident with points in the other, overlapping point clouds.
一种更强大的替代方法是同时使用多个波长直接从激光雷达获得光谱信息。组合使用两个波长的概念并不是特别新的。实际上,多波长激光雷达用于测深应用是一种旧技术,其原理于1965年首次介绍。传统上,这些系统有两个波长,一个在电磁谱的近红外部分(1,064)(1,064NM),一个在绿色(532nm)中。之所以这样做,是因为红外光束反映了海面的反映,因此可以轻松识别水在哪里遇到空气。绿光束(532nm)穿过水面,用于定位海床。但是,由于这些系统的设计并非旨在提取有关它们所反映的表面的光谱信息,因此无法准确分析光谱签名的差异并具有有意义的使用。最新的发展包括使用Optech的CZMIL系统生产的放射线校正仪器以及先前的Shoals系统。
三个波长
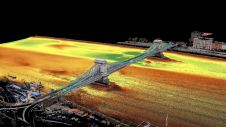
2014年12月,Optech宣布第一个像rcially available multispectral Lidar system, the Optech Titan. This system combines three separate wavelengths along a single optical path. The wavelengths are positioned in the green (532nm) and infrared (1,064nm and 1,550nm) parts of the spectrum. The system is designed to suit a range of applications such as high-density topographic surveying, shallow water bathymetry, environmental modelling, urban surface mapping and land cover classification. As the three beams do not pass along the exact same path in space, the points recorded for the Titan system do not lie in exactly the same place in 3D space. This means that a user collects three independent point clouds, each relating to a different laser wavelength. These can then be combined through a gridding process, resulting in a raster rather than a point cloud. Figure 2 shows a gridded point cloud from the Titan system, visualised in false colour to represent all wavelengths.
进一步的改进
最终的多光谱激光雷达将提供一个point cloud whereby each point is recorded in each of the three wavelengths. To do so, manufacturers will have to make a system where the beams overlap precisely and the returns are measured simultaneously. Consistent calibration across the different wavelengths must be maintained, and interpreting the signal can be challenging because three waveforms have to be processed simultaneously. Once these technical challenges have been overcome, however, the benefits will be enormous. Spectral information will be available for everything that the Lidar system can measure, not just the very top surface. This is particularly important when mapping natural surfaces where there is a presence of vegetation. This technology will allow identification of differences between materials at all points where the laser has reached the surface plus it will offer all the advantages of an active system.
Applications in forest mapping
该公司Carbomap是爱丁堡大学的衍生产品,它为林业应用程序处理了多光谱激光雷达数据。具体而言,在该区域使用了多光谱的激光雷达来识别地面层以及叶子和木材之间的区分。可以以这种方式得出更准确的信息,可以进行更准确的生物量估计,并且生物量估计对于REDD+(减少森林砍伐和退化)监测至关重要。
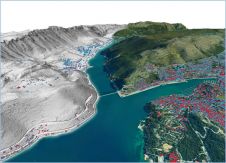
另一个应用程序是使用多光谱的激光雷达来创建弯曲的森林冠层图。Carbomap在实践中对此进行了测试。来自RIEGL USA的三个机载激光雷达系统具有不同的波长(532nm,1,064nm和1,550nm),在美国弗吉尼亚州的森林上飞行在同一平台上。Carbomap的处理软件用于将每个波长数据集中的最接近的LIDAR点绑定。随后,创建了三通道假颜色复合材料。图3显示了从不同波长返回的能量之比。这证明了垂直森林冠层内的光谱变化量,这又使专家可以绘制底层的健康和树种。该方法的应用包括火灾风险管理和入侵物种的映射。LiDar的未来在于多光谱系统的进一步进步。这样的技术飞跃将为新的用途和应用铺平道路,使多光谱激光雷达的未来确实非常令人兴奋。
作者
Sam Fleming
萨姆·弗莱明(Sam Fleming)是伦敦大学学院的硕士学位和英国爱丁堡大学的地理学士学位的遥感专家。他的专业知识在于利用有关森林的LiDar数据来提取结构参数。他最近在Greenstone担任碳顾问。
Iain H. Woodhouse
Iain H. Woodhouse is lead co-inventor of the multispectral canopy Lidar. He is a professor of applied Earth observation at the University of Edinburgh, UK. In 2008 he co-founded Ecometrica and was a non-executive director from 2008-2012. In 2009 Iain founded REDD Horizon, a capacity-building programme in Malawi. In 2012 Iain was funded by a Royal Society of Edinburgh Enterprise award to help set up Carbomap.
Antoine Cottin
Antoine Cottin is an expert in bathymetric Lidar processing. He did his PhD in Quebec, Canada, and then a postdoc working in Mississippi, USA, with Optech and the US Army Corp of Engineers. He has a decade of experience in processing full waveform systems. Antoine has also led teams in successful field campaigns and has experience in the application and processing of terrestrial laser scanners.